[Git] Branch Management & Workflows
以下部份翻譯ProGit 中文版v1 / 英文版v2, 加上自己一些測試。
git branch -v 可以察看每個branch最新的commit
$ git branch -v
iss53 93b412c fix javascript issue
* master 7a98805 Merge branch 'iss53'
testing 782fd34 add scott to the author list in the readmes
git branch --merged 和 git branch --no-merged察看哪些branch已經merge或是還沒
git branch -d testing會提示該branch還未merge, 若真的要delete要用git branch-D
Long-Running Branches 長期分支
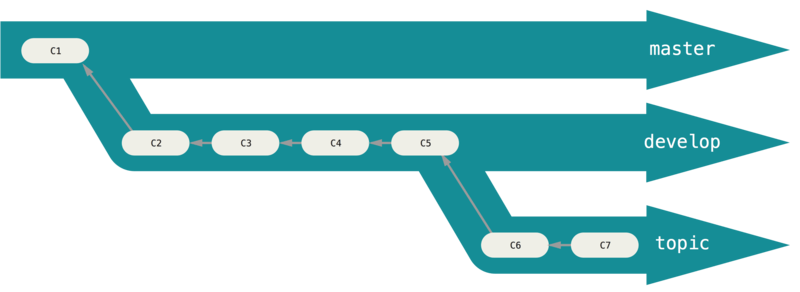
master -- possibly only code that has been or will be released.
develop -- 不一定stable, 但是有達到stable state後, 就會把他merge到master
topic --- 像iss53, 通過測試並且不會產生bug後, 在合併到develop去
branch事實上就是討論指標的移動, stable branches 指標總是在主線的很後面, 而前沿分支總是比較靠前:

Some larger projects also have a proposed or pu (proposed updates) branch that has integrated branches that may not be ready to go into the next or master branch. The idea is that your branches are at various levels of stability; when they reach a more stable level, they’re merged into the branch above them.
Again, having multiple long-running branches isn’t necessary, but it’s often helpful, especially when you’re dealing with very large or complex projects.
multiple Topic Branches
任何大小的project都適用
你可以把作出的改變保持在特性分支中幾分鐘,幾天甚至幾個月,等它們成熟以後再合併,而不用在乎它們建立的順序或者進度。
例如以下我們先在master工作到C1, 開新branch處理iss91問題, 做到C6的時候, 又冒出可以解決該問題的新方法, 又回到C4分出分支iss91v2, 做到C8的時候, 又回到主幹master提交了C9和C10, 再回到iss91v2工作, 提交C11, 再來又冒出不太確定的想法, 從master的C10又開了新的分支dumbidea做實驗:
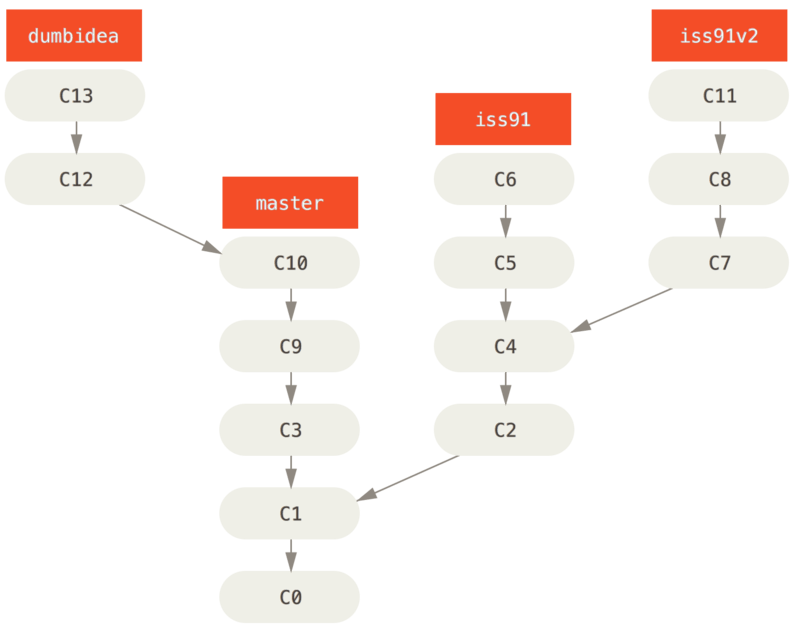
最後決定使用第二個解決方案iss91v2, 另外也保留dumbidea, 那我們就拋棄iss91(就是捨棄C5和C6), 在master中把iss91v2和dumbidea合併, 最後的commit history會變成如下:
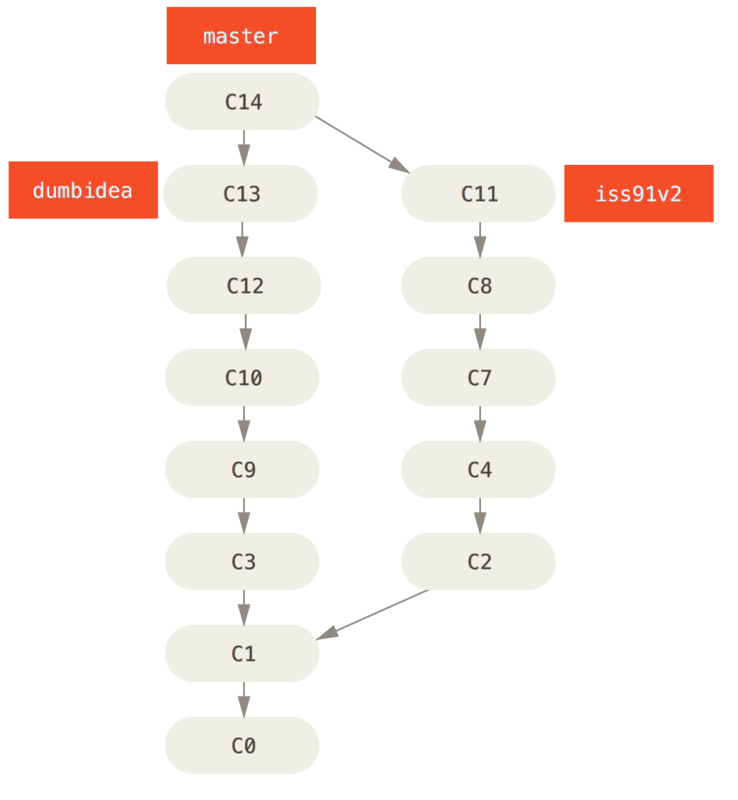
要決定採用哪種branching scheme, 要確認讀了Git distributed workflow